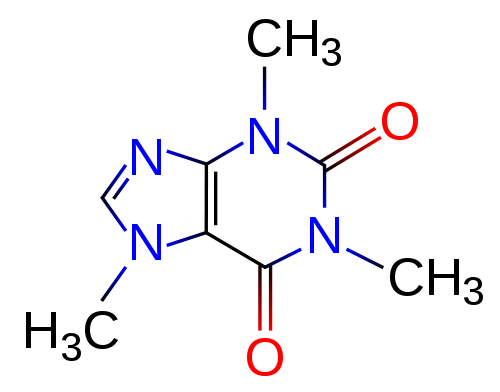
Caffeine is classed as a methylxanthine, together with theobromine and theophylline. Of those three chemical compounds, caffeine had the best stimulant impact on the central nervous system and the skeletal muscle mass, and the least impact on the cardiovascular system.
The absorption of caffeine is fast. Its results take about half-hour, which is the time the height blood ranges are reached. Maximal central nervous system results take about 2 hours and caffeine’s half-life is about 3 hours. (Keep in mind the 10-2 and 4 adverts for Dr. Pepper?) It’s metabolized virtually fully, with solely 10% or much less being excreted from the physique unchanged.

Dr. Pepper 10-2-4 Classic Signal signal by Brent Moore
Caffeine’s stimulant motion on the central nervous system is attributable to its capacity to dam the mind’s neuroreceptors for adenosine. Adenosine itself acts as a neuromodulator to supply behavioral sedation in a number of areas of the mind by inhibiting the discharge of neurotransmitters. By inhibiting adenosine’s sedative results, caffeine causes stimulation.
Low doses of about 200 mg of caffeine trigger decreased drowsiness and fatigue in most people. The stimulant impact on skeletal muscle mass will increase the physique’s capacity to carry out bodily exhausting work for longer durations of time. The identical dose of 200 mg retains most individuals awake longer and causes sleep disturbances.
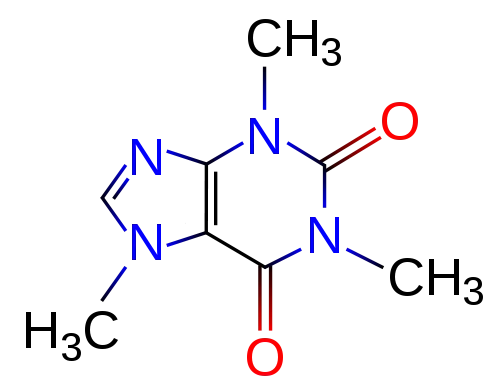
Caffeine Molecule
Caffeine’s stimulant qualities precipitated the Nationwide Academy of Sciences’ Institute of Medication to advocate methods so as to add caffeine to U.S. troopers’ rations. Since caffeine would possibly give an athlete an unfair benefit, the U.S. Olympic Committee considers it a “efficiency enhancer”, and commonly screens athletes for the drug.- from a paper introduced at Penn State College by Robert L. Badgett- additionally printed in Badgett’s Espresso eJournal, Problem 4, June 16, 2000
Printed on


